Traditional single-building energy studies have limitations, as buildings interact with each other through heat and radiation exchange, leading to unexpected energy consumption. Urban Building Energy Modeling (UBEM) aims to enhance city sustainability through performance-based design. However, it is complex and challenging for practitioners to implement the simulation.
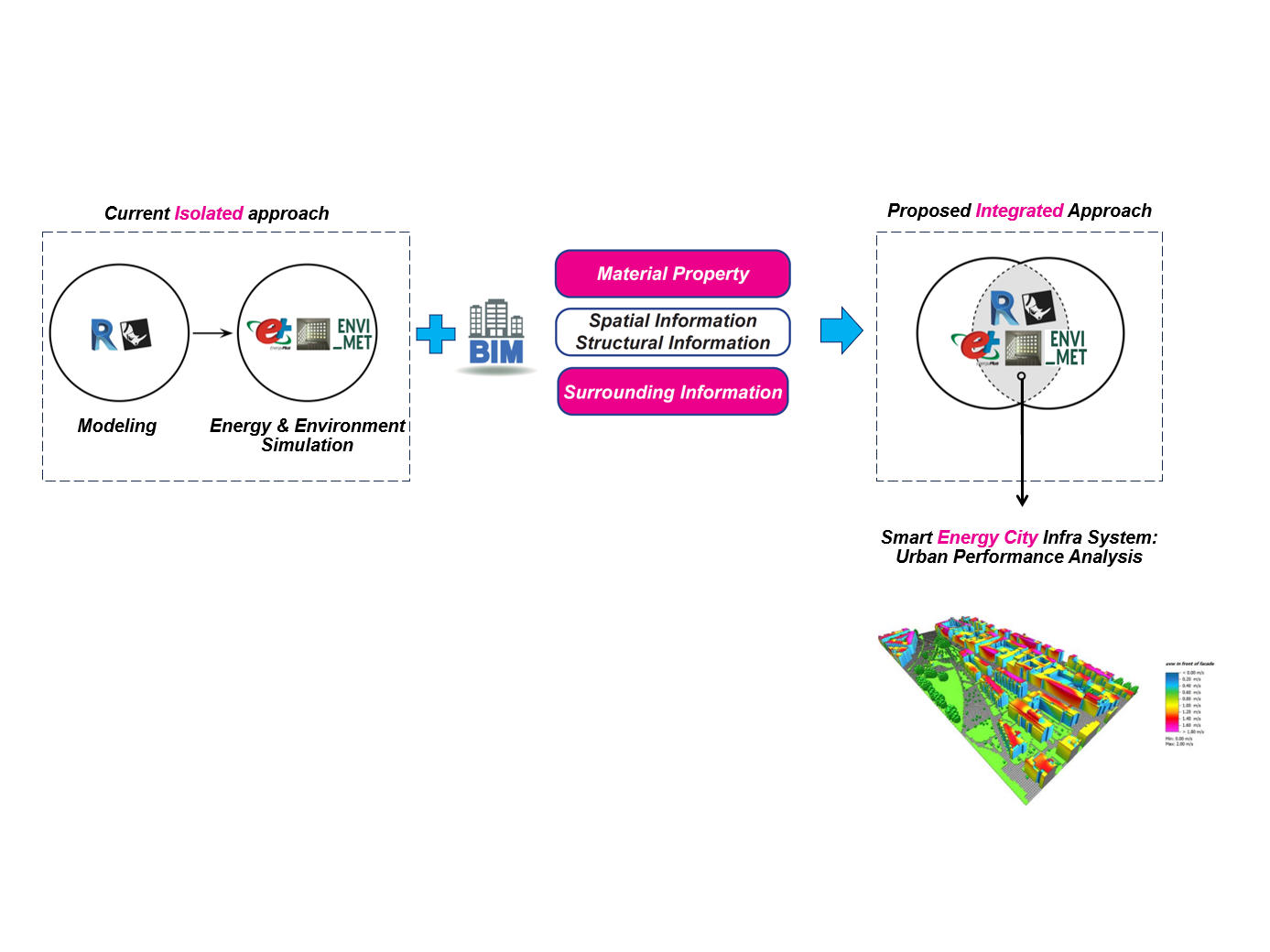
Currently, the urban design/planning and evaluation processes have been disconnected. As a result, building and urban design often proceed without performance evaluations. To bridge this gap, we have developed an AI-based system to surrogate complex simulations. The system automatically extracts necessary data from the BIM and uses it as inputs for AI to predict outdoor conditions on behalf of practitioners.
This integrated system will be further developed to build a Smart Energy City Infrastructure System so that we can assess current urban design/planning problems and explore solutions in terms of energy savings and carbon neutrality.
과거 연구는 에너지 분석을 위해 한 건물을 집중적으로 시뮬레이션을 시행하였습니다. 하지만 실제 건물은 서로 열 교환 작용을 통해 상호작용을 하고 서로 영향을 미칩니다. 그렇기에 과거의 방식은 시뮬레이션 값과 실제 소비량에 큰 오차가 있었습니다. 하여 최근 들어 도시건물 에너지 모델링에 그 초점이 맞춰져 있으나 이는 너무 복잡하기에 실무자들이 도시 설계/계획을 할 때 환경 분석을 반영하는데 어려움이 있습니다.
현재 건물과 도시 모델링과 환경평가는 각기 다른 과정으로 인식되고 있습니다. 하여 많은 경우 환경평가가 무시된 채 건물과 도시가 설계/계획되고 있습니다. 이 문제점을 해결하기 위해 인공지능을 통해 복잡한 도시 건물에너지 모델링을 대리 모델로서 학습하고 실무자 대신 환경평가를 자동으로 해주는 시스템을 개발했습니다.
이를 바탕으로 미래에 스마트 에너지 시티 기반 시스템을 만들고 이로써 현재의 도시 설계/계획의 저탄소 목표 달성에서의 에너지 효율 문제점을 파악하고 그 대안들을 살펴볼 수 있게 하고자 합니다.
